Anjing Road, Xiaolan, Zhongshan, Guangdong, China
info@mes-drive.com
08.00 AM-09.00 PM
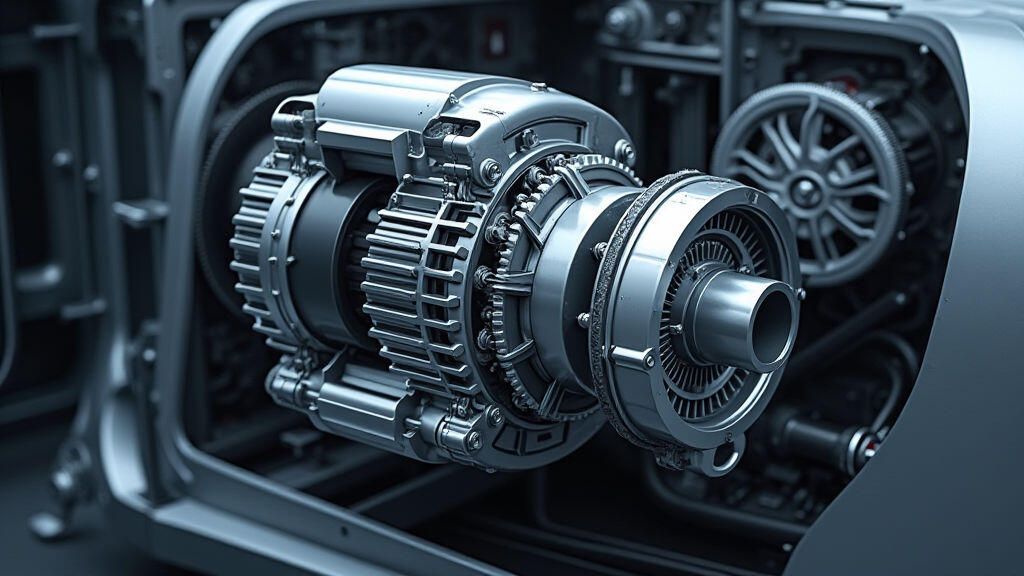
In late September 2025 the world witnessed a historic milestone: global electric‑vehicle (EV) sales surged to a record 7.5 million units, according to a Reuters report. The surge was driven by a coalition of new government incentives—from the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act’s tax credits to the European Green Deal’s plug‑in mandate—together with aggressive supply‑chain scaling in China and a vibrant start‑up sector in Africa. Amid the headline‑grabbing headlines and soaring stock prices, one unassuming component has quietly become the backbone of this revolution: the gear motor, also known as the reducer motor. Below we explore how these compact powerhouses are turning policy ambition into road‑worthy reality, and why their role will only grow as nations race toward net‑zero.

At first glance, a gear motor looks like an unremarkable block of metal. In truth, it combines an electric motor and a set of gears that reduce the high‑speed, low‑torque output of the motor to a more usable torque‑rich speed for the wheel. This reduction not only improves acceleration but also extends the motor’s operational life, making gear motors the preferred choice for most front‑ and rear‑wheel‑drive EVs worldwide.
Unlike large, planet‑gear planetary gear sets used in heavy duty trucks, the gear motors in passenger cars are typically geared torque motors (GTM) with a reduction ratio between 5 : 1 and 20 : 1. The reduced speed results in a power density that matches the car’s wheel‑speed requirements, while the integrated gearing eliminates the need for an external gearbox, saving weight and space—both critical variables in fuel‑efficient EV design.
When Tesla first unveiled its Model S in 2020, the company used a half‑size, “Motor and Gearbox in one” assembly. This modular approach, pioneered by the newly formulating gear motor industry, evolved into the GTM standard that powers the vast majority of electric cars today. The simplicity of the drivetrain, combined with lower maintenance downtime, has been a decisive factor in the EV market’s explosive adoption. The very same gear motor architecture is now being scaled up for medium‑size electric buses and heavy‑load delivery vans, further cementing its standing in the electrification ecosystem.
The European Union’s Green Deal announced a legally binding 80 % cut in EU‑wide CO₂ emissions by 2050. A cornerstone of this agenda is the “Fit for 55” package, which stipulates that all passenger cars sold in the EU must be zero‑emission by 2035. This deadline pushes European carmakers to accelerate their EV roadmaps, and by extension, to adopt efficient gear motor technology to keep costs competitive.
Recent EU‑backed research grants for “Smart Graded Powertrains” focus on developing lower‑friction, higher‑precision gear motors capable of integrating power‑train diagnostics via the vehicle's CAN‑bus. Such gear motors can actively communicate their load, temperature, and wear states to the car’s central computer, enabling predictive maintenance that reduces repair costs and downtime—an attractive proposition for fleet operators looking to keep their vehicles on the road.

China’s increasing electric freight market—particularly the "EleBots"—has required a steady stream of high‑quality gear motors. The state‑owned manufacturer Boshoku, along with its joint venture with interior design giant Sajama, is investing $300 million to establish a green twin‑motor factory. Early prototypes incorporate 3‑D‑printed metallic gear teeth with a ceramic coating that reduces wear by 40 %, a breakthrough that promises to extend the lifespan of gear motors in aggressive delivery fleets.
There is a feedback loop between economies and technology: as China's gigafactories scale up battery output, gear motor demand spikes, which in turn motivates peripheral suppliers—metal alloys, bearings, and heat‑sinks—to innovate. The result is a cascade of incremental improvements that bring down the cost per watt. For instance, across 2025, the 5 kW gear motor price fell from $530 to $420, a 20 % reduction that carmakers have fed straight into price‑competitiveness for new electric models.
Beyond cars, gear motors are integral to the robotics and autonomous vehicle sectors that have become flashpoints in 2025, especially after the Tesla Automation Conference in Austin, Texas. The conference spotlighted a new generation of 1 kW micro‑gear motors designed specifically for manufacturing robots requiring precise position control and high torque in a lightweight package.
The 2025 model labels its “Zero‑Loss Torque Peak” (ZTP) technology: a combination of lightweight meshing design and an adaptive gearing algorithm that tackles back‑drifting during high torque stops. Though initially marketed for industrial applications, many EV developers are evaluating micro‑gear motors for cycling propulsion (e‑cycles) and personal air‑mobility, expanding the gear motor’s horizon beyond conventional automotive use.
Artificial intelligence is now being applied to gear motor design itself. Advanced machine‑learning algorithms traverse millions of gear tooth geometries and predict friction coefficients under various load conditions, enabling designers to shave material waste while guaranteeing longevity. At the same time, graphene‑infused composites are arriving in production trucks, promising lighter, stronger gear assemblies with temperatures that remain stable under friction heat.
For consumers, the benefit is an instant one‑set‑off acquisition of an electric vehicle that is not just greener but also more reliable. For the industry, it’s a win–win for cost, efficiency, and sustainability. The 2025 announcement by the International Energy Agency that “reducing transmission losses" will be a top ten technology metric—already linked to gear motor performance—underscores the field’s significance.
From policy to product, gear motors sit at the heart of 2025’s accelerating shift toward zero‑emission transportation. Policy mandates like the EU Green Deal and U.S. tax incentives have spurred a mass purchasing wave, while Chinese manufacturers’ rapid scaling has *kept the supply chain humming*. Intelligent design, AI‑augmented material science, and micro‑scale innovations are removing the barriers of cost and performance that once made EVs a niche market.
In the end, the gear motor—simple in form but sophisticated in function—remains the unseen hero that translates ambitious levers of climate policy into the everyday experience of driving in a cleaner, quieter world. As we move toward 2030 and beyond, the evolution of gear motors will continue to drive the automotive industry’s transformation, ensuring that the ascent to net‑zero is powered, quite literally, by the humble reducer motor.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked